Erstellen Sie eine Instanz RancherOS: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Ikbot (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Ikbot (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 14: | Zeile 14: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell | + | Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. Sie können den Artikel Quelle [[:fr:Creer une instance RancherOS|hier]] ansehen.<br /><span data-translate="fr"></span> |
Version vom 10. Dezember 2015, 11:28 Uhr
he:ליצור מופע RancherOS
ro:Creaţi o instanţă huevos
ru:Создайте экземпляр RancherOS
pl:Utworzenie wystąpienie RancherOS
ja:ランチャロス インスタンスを作成します。
ar:قم بإنشاء مثيل رانتشيروس
zh:创建一个实例牧场主人
nl:Een exemplaar maken RancherOS
it:Creare un'istanza RancherOS
pt:Criar uma instância RancherOS
es:Crear una instancia de RancherOS
en:Create an instance RancherOS
fr:Creer une instance RancherOS
Dieser Artikel wurde maschinell übersetzt. Sie können den Artikel Quelle hier ansehen.
Das folgende Verfahren beschreibt das Erstellen einer Instanz RancherOS Ikoula Wolke. RancherOS ist die GNU-Distribution /Linux ist das weitere minimalistische und Hafenarbeiter benutzerfreundlich. Alles ist im RancherOS Container (z.B. von Udev und Rsyslog ), Docker läuft auch als Prozess PID 1 Dieses System (in der Regel Init oder Systemd ). Es ist auch ein System, das hat den Vorteil, dass die neueste Version von Docker oder fast so interessant, wenn Sie die neuesten Features von Docker haben möchten.
In einem ersten Schritt eine Verbindung zu die Verwaltungsoberfläche Ikoula Wolke :
Erstellen einer neuen Instanz :
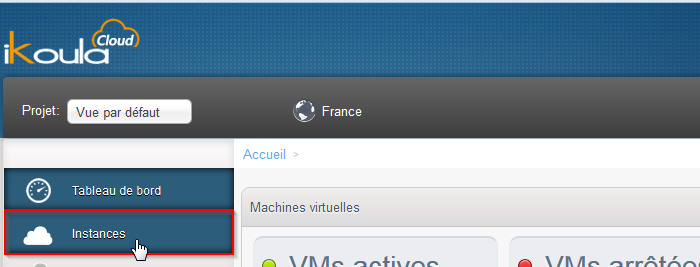
- Klicken Sie auf "Stellen" im linken Menü vertikal :
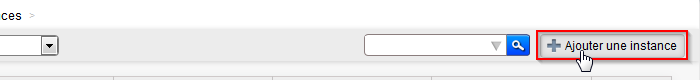
- Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche 'Hinzufügen eine Instanz' :
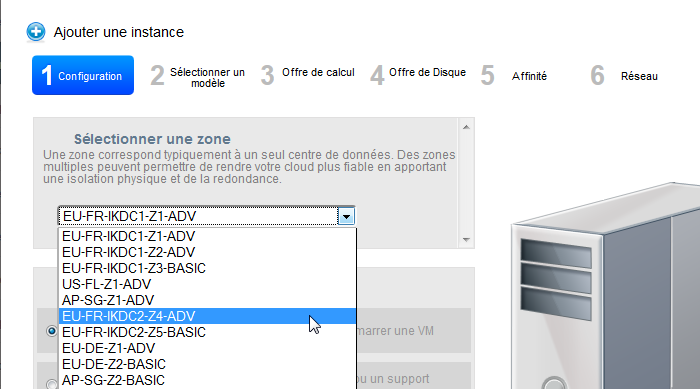
- Wählen Sie im Dropdown-Listenfeld eine Bereitstellung (in unserem Beispiel wählen wir eine Zone erweiterte vernetzten / Name des Bereichs endet mit "ADV" ) :
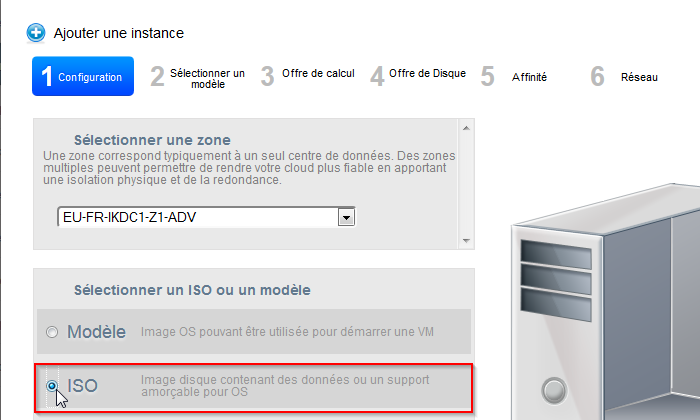
- Wählen Sie "ISO" :
- Klicken Sie auf «weiter»
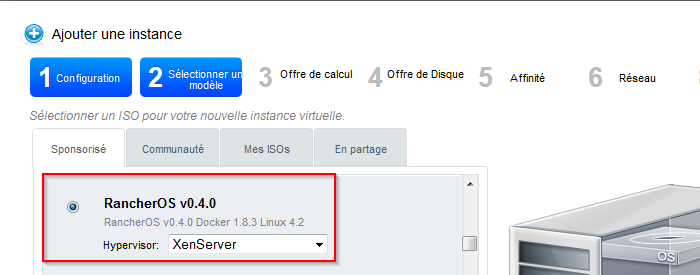
- Wählen Sie die ISO "RancherOS V 0.4 '. "in der Liste der ISO der gesponserten Registerkarte :
- Klicken Sie auf «Weiter»
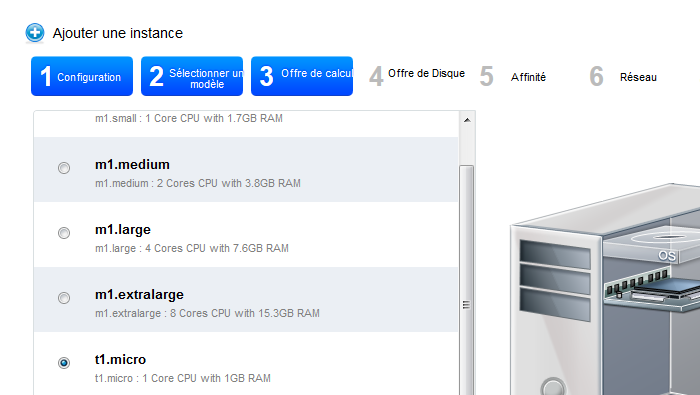
- Wählen Sie ein Angebot der Berechnung :
- Klicken Sie auf «Weiter»
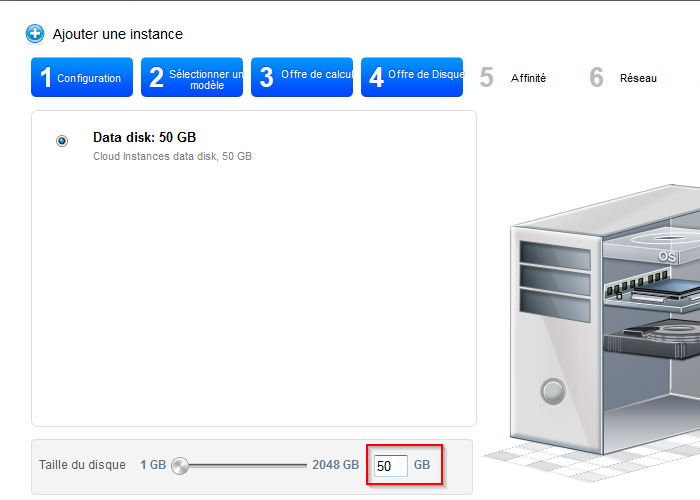
- Geben Sie die Größe, die Sie auf das virtuelle Laufwerk zuweisen (Rootdisk ) die Instanz :
- Klicken Sie auf "weiter" zweimal
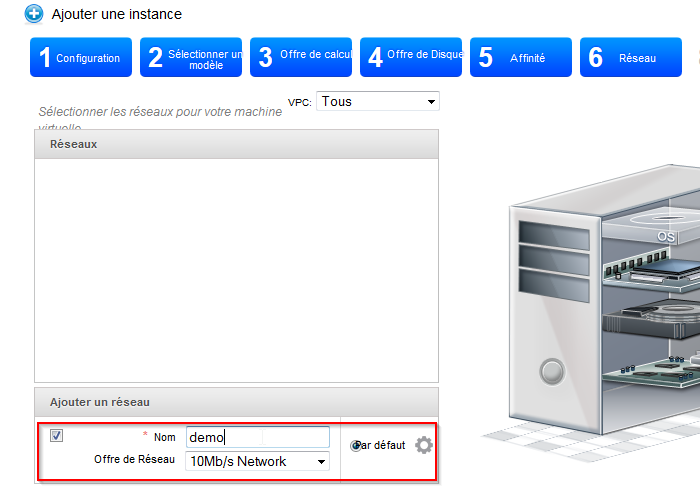
- Ein Netzwerk hinzufügen, indem Sie einen Namen und das gewünschte Netzwerk-Angebot eingeben oder wählen Sie eine der vorhandenen Netze :
- Klicken Sie auf "Folgende"
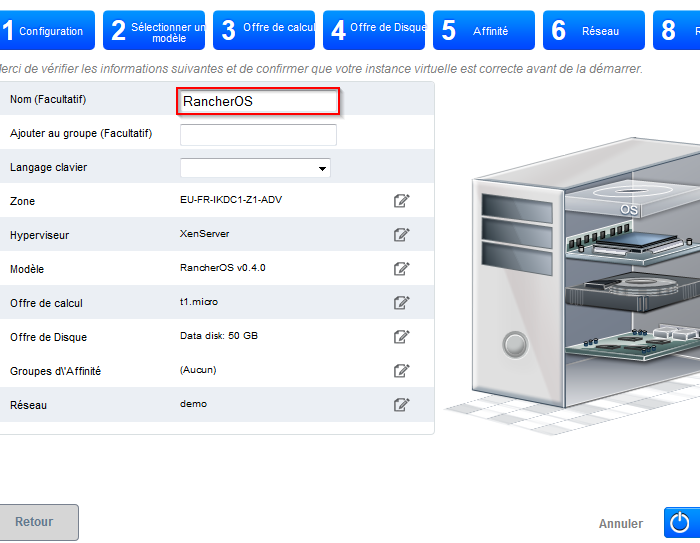
- Definieren Sie einen Namen für die Instanz, und klicken Sie dann auf die Schaltfläche "Start VM" :
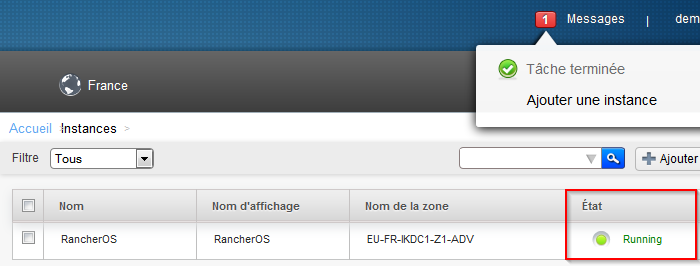
- Warten Sie, bis die Instanz 'ausgeführt' :
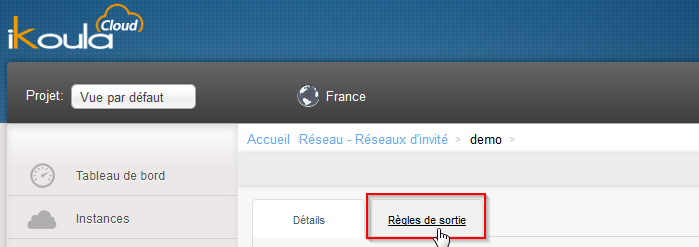
- Klicken Sie auf "Netzwerk" im linken Menü vertikal auf das Netz von den Namen der Instanz, und klicken Sie dann auf 'Exit-Regeln' :
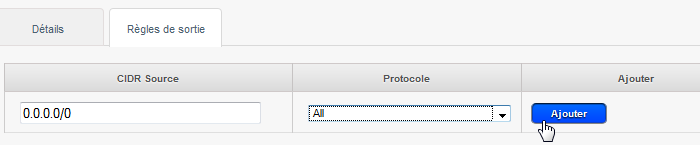
- Ausgabe-Regel hinzufügen (Firewall ) den Abfluss für alle Protokolle autorisieren :
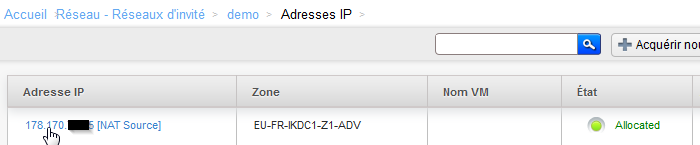
- Gehen Sie zurück zur Registerkarte "Details" des Netzwerks, und klicken Sie auf "Finden Sie unter IP-Adressen" IP NAT Quelle, Ihre Netzwerkadresse :
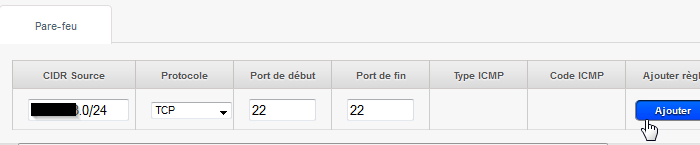
- Klicken Sie auf die Registerkarte " '. Konfiguration "dann klicken Sie auf 'Alle anzeigen' Firewall und hinzufügen eine eingehenden Firewallregel SSH-Verbindungen erlaubt (Hafen 22/TCP ) zu Ihrem Netzwerk
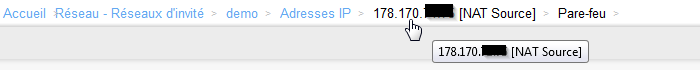
- Neu click auf die Quell-Ip Adresse NAT des Netzwerks :
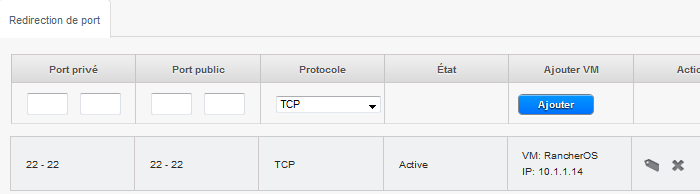
- Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche "Alle anzeigen" Port-Weiterleitung, dann fügen Sie eine Port-Weiterleitungsregel so dass Sie in Ihrer Instanz in SSH einloggen (ab : Private Port 22 öffentlicher Port 22 Protokoll TCP ) und fügen Sie Ihre Instanz und machen 'Anwenden'
- Anmelden in ssh verbunden mit der Instanz mit der "Viehzüchter" Login und Passwort "Viehzüchter" Iso :
demo@pc-demo:~$ ssh rancher@178.170.XX.XX
The authenticity of host '178.170.XX.XX (178.170.XX.XX)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is xx:85:xx:02:xx:bf:xx:b4:xx:1d:xx:1a:xx:3a:xx:0b.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '178.170.XX.XX' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
rancher@178.170.XX.XX's password:
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$
- Erstellen Sie eine Datei Wolke-config.yml mit Client öffentlichen SSH RSA Ihres Schlüssels Arbeitsstation. Es ist dieser Schlüssel, der Ihnen erlaubt, mit den "Viehzüchter" ssh einloggen Ihre RancherOS Herstellen einer Instanz (finden Sie unter http://docs.rancher.com/os/Wolke-config/) :
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$ cat << EOF > cloud-config.yml
> #cloud-config
> ssh_authorized_keys:
> - ssh-rsa AAAAB...XXXXXX...YYYY.....ZZZZdemo@pc-demo
> EOF
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$
Ersetzen "AAAAB...XXXXXX...YYYY.....ZZZZdemo@pc-demo" von der wichtigsten öffentlichen SSH-Rsa Ihre Client-Workstation im obigen Beispiel.
- Einmal die Datei Wolke-config.yml erstellt haben, führen Sie den Befehl " '. Sudo installieren - C Ros Wolke-config.yml - d /dev/xvda » RancherOS auf dem virtuellen Laufwerk installieren (Rootdisk ) die Instanz :
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$ sudo ros install -c cloud-config.yml -d /dev/xvda
INFO[0000] No install type specified...defaulting to generic
Installing from rancher/os:v0.4.1
Continue [y/N]: y
Unable to find image 'rancher/os:v0.4.1' locally
v0.4.1: Pulling from rancher/os
26b82ec3311d: Pull complete
f05335696a9b: Pull complete
8e8fa9d5f794: Pull complete
6cbde7cc282e: Pull complete
ed08d2a1b7fe: Pull complete
3b09e65b0985: Pull complete
87bbc662b44c: Pull complete
f17c535a2c45: Pull complete
f5261f101133: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:320addc8d74521965956b8ec97c025b3d79db2f1e1a83235b767fe0953ef5b88
Status: Downloaded newer image for rancher/os:v0.4.1
+ DEVICE=/dev/xvda
+ [[:fr: -z /dev/xvda ]]
++ wc -l
+++ cut -d / -f3
+++ echo /dev/xvda
++ grep xvda /proc/partitions
+ PARTITION_COUNT=1
+ '[' 1 -gt 1 ']'
+ dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/xvda bs=512 count=2048
2048+0 records in
2048+0 records out
1048576 bytes (1.0 MB) copied, 0.0372273 s, 28.2 MB/s
+ partprobe /dev/xvda
+ fdisk /dev/xvda
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.25.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table.
Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x5ab88c99.
Command (m for help): Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): Partition number (1-4, default 1): First sector (2048-104857599, default 2048): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-104857599, default 104857599):
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 50 GiB.
Command (m for help): The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
++ dirname /scripts/lay-down-os
+ . /scripts/build.conf
++ IMAGE_NAME=rancher/os
++ VERSION=v0.4.1
++ DOCKER_BINARY_URL=https://github.com/rancher/docker/releases/download/v1.9.1-rc1-ros1/docker-1.9.1-rc1
++ COMPILED_KERNEL_URL=https://github.com/rancher/os-kernel/releases/download/Ubuntu-4.2.0-16.19/linux-4.2.3-rancher-x86.tar.gz
++ DFS_IMAGE=rancher/docker:1.9.1-rc1
+ VERSION=v0.4.1
+ getopts i:f:c:d:t:r:o:p: OPTION
+ case ${OPTION} in
+ DEVICE=/dev/xvda
+ getopts i:f:c:d:t:r:o:p: OPTION
+ case ${OPTION} in
+ ENV=generic
+ getopts i:f:c:d:t:r:o:p: OPTION
+ case ${OPTION} in
+ CLOUD_CONFIG=/opt/user_config.yml
+ getopts i:f:c:d:t:r:o:p: OPTION
+ DIST=/dist
+ CLOUD_CONFIG=/opt/user_config.yml
+ CONSOLE=tty0
+ BASE_DIR=/mnt/new_img
+ PARTITION=/dev/xvda1
+ KERNEL_ARGS=
+ '[' -n generic ']'
+ case ${ENV} in
+ format_and_mount
+ format_device
+ device_defined /dev/xvda
+ [[ -z /dev/xvda ]]
+ mkfs.ext4 -F -i 4096 -L RANCHER_STATE /dev/xvda1
mke2fs 1.42.12 (29-Aug-2014)
Creating filesystem with 13106944 4k blocks and 13107200 inodes
Filesystem UUID: 704a1b35-b886-430e-be0c-fac8e3ca5237
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
+ mount_device
+ local label=RANCHER_STATE
+ local raw=false
+ mkdir -p /mnt/new_img
++ wc -l
++ grep RANCHER_BOOT
++ lsblk -o name
+ '[' 0 -eq 1 ']'
+ local 'mount_opts=-L RANCHER_STATE'
+ '[' false == true ']'
+ mount -L RANCHER_STATE /mnt/new_img
+ trap 'umount /mnt/new_img' EXIT
+ create_boot_dirs
+ mkdir -p /mnt/new_img/boot/grub
+ install_grub
+ grub-install --boot-directory=/mnt/new_img/boot /dev/xvda
Installing for i386-pc platform.
Installation finished. No error reported.
+ /scripts/seed-data /mnt/new_img /opt/user_config.yml
+ BASE_DIR=/mnt/new_img
+ CLOUD_DATA=/opt/user_config.yml
+ IFS=,
+ read -ra FILES
+ '[' -z /mnt/new_img ']'
+ mkdir -p /mnt/new_img/var/lib/rancher/conf/cloud-config.d
+ '[' /opt/user_config.yml '!=' /scripts/conf/empty.yml ']'
+ cp /opt/user_config.yml /mnt/new_img/var/lib/rancher/conf/cloud-config.d/
+ grub2_config ''
+ local grub_cfg=/mnt/new_img/boot/grub/grub.cfg
+ local append_line=
+ cat
+ '[' '!' -z ']'
+ pvgrub_config ''
+ local grub_file=/mnt/new_img/boot/grub/menu.lst
+ local append_line=
+ cat
+ '[' '!' -z ']'
+ install_rancher
+ cp /dist/initrd /mnt/new_img/boot/initrd-v0.4.1-rancheros
+ cp /dist/vmlinuz /mnt/new_img/boot/vmlinuz-v0.4.1-rancheros
+ umount /mnt/new_img
Continue with reboot [y/N]: y
INFO[0103] Rebooting
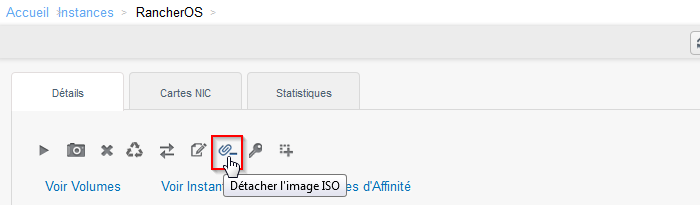
- Beenden Sie die Instanz und trennen die ISO es :
- Die Instanz gestartet, nachdem die ISO von diesem getrennt
- Verbindung mit Ihrer Instanz RancherOS in ssh mit Login 'Viehzüchter' aus der Maschine, die den öffentlichen SSH-Schlüssel hat, die Sie zu der Datei hinzugefügt Wolke-config.yml oben :
demo@pc-demo:~$ ssh rancher@178.170.XX.XX
The authenticity of host 178.170.XX.XX (178.170.XX.XX)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is xx:66:xx:c5:xx:bf:xx:b4:xx:47:xx:1a:xx:b8:xx:cf.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '178.170.XX.XX' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$
- Die Instanz hat nun RancherOS Disk :
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$ docker info
Containers: 0
Images: 0
Server Version: 1.9.1-rc1
Storage Driver: overlay
Backing Filesystem: extfs
Execution Driver: native-0.2
Logging Driver: json-file
Kernel Version: 4.2.3-rancher
Operating System: RancherOS (containerized)
CPUs: 1
Total Memory: 990.8 MiB
Name: RancherOS.CloudInstances
ID: CWVI:BCAE:3DPO:2TCG:JKHM:RFVS:47G2:LZOH:4GB3:SP2Z:4A66:AVF7
[rancher@RancherOS ~]$
[root@RancherOS rancher]# df -hT
Filesystem Type Size Used Available Use% Mounted on
overlay overlay 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /
tmpfs tmpfs 482.0M 0 482.0M 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 495.4M 0 495.4M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /home
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /opt
none tmpfs 495.4M 272.0K 495.1M 0% /run
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/iptables
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/poweroff
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /lib/modules
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/halt
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/shutdown
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/docker
none tmpfs 495.4M 272.0K 495.1M 0% /var/run
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/rkt
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /sbin/reboot
devtmpfs devtmpfs 482.0M 0 482.0M 0% /host/dev
shm tmpfs 64.0M 0 64.0M 0% /host/dev/shm
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /lib/firmware
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/log
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/ros
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/lib/rancher
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/system-docker
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/wait-for-docker
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/netconf
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/user-docker
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/rancherctl
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/dockerlaunch
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/respawn
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/lib/rkt
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/sbin/wait-for-network
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/docker.dist
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/bin/cloud-init
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/lib/docker
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /usr/share/ros/os-config.yml
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /var/lib/rancher/conf
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt.rancher
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/resolv.conf
/dev/xvda1 ext4 46.7G 235.3M 44.0G 1% /etc/hostname
shm tmpfs 64.0M 0 64.0M 0% /dev/shm
devtmpfs devtmpfs 482.0M 0 482.0M 0% /dev
shm tmpfs 64.0M 0 64.0M 0% /dev/shm
[root@RancherOS rancher]#
Sie können, wenn Sie eine Vorlage Ihrer Instanz von der Rootdisk andere RancherOS bereitstellen möchten (ex: Cluster RancherOS /Docker)
Die automatische Aktualisierung der Kommentare aktivieren.